Genetic copying is the process of taking DNA from one organism and inserting it into another. This can be done in many ways, but the most common way is through genetic engineering. Genetic engineering involves using enzymes to cut out a piece of DNA from one organism and insert it into another.
Genetic copying has been used for many years now, but it’s still controversial because of its potential dangers:
The benefits of genetic copying are numerous. For example, it can be used to preserve endangered species by cloning them and then releasing them back into the wild. It has also been used in medicine to help treat diseases such as cancer and diabetes. In addition, genetic copying has allowed us to create medicines that are tailored specifically for each individual patient’s needs based on their DNA makeup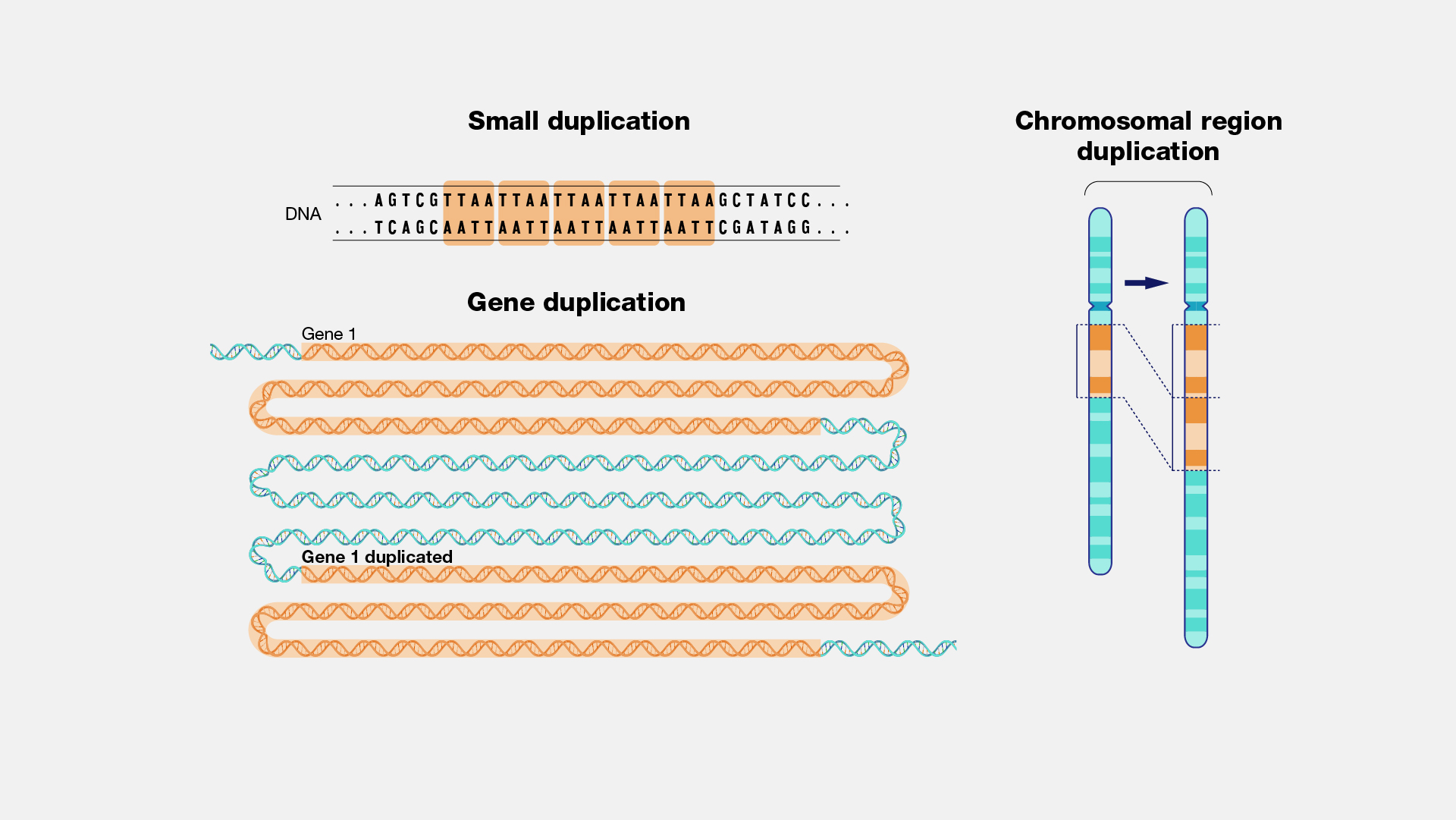
Genetic copying is a fascinating concept, but it’s not without its drawbacks. Here some of them:
- Ethical concerns. Some people have ethical objections to genetic copying because they feel it’s unnatural or unethical to create humans in this way. And also some of them think that these genetic copying can be used by countries to make the perfect soldier, army, super human that will bring destruction.
- Lack of genetic diversity. If you’re going to clone yourself, your child will be genetically identical to you which means there will be no variation between them at all. This can lead to problems down the line if something happens that needs fixing (like an illness). Without any diversity in their DNA, there won’t be any backup plans available if one gene fails, instead, everything will fail at once because everyone has exactly the same genes as each other.

The risks and benefits of genetic copying are many. It’s important to consider both sides before making a decision about whether or not you want to use this technology in your own life.
If you do decide to go ahead with it, there are some things that you should know:
- Genetic copying can be dangerous if done incorrectly or without proper training. You should always consult with an expert before attempting any kind of genetic copying yourself.
- The success rate for cloning is 50%, meaning half of all clones survive the process and live healthy lives; the other half die during birth or shortly thereafter due to complications caused by their undeveloped brains being unable to sustain life outside their mother’s womb.

